How Your Gut Influences Estrogen: Understanding the Estrobolome
When most of us think about estrogen, we picture our ovaries as the main source of this powerful hormone. But there’s another surprising player in the story: your gut.
The trillions of microbes living in your digestive tract don’t just break down food. They also help regulate how much estrogen is circulating in your body, influencing everything from mood and metabolism to bone strength and disease risk.
At the heart of this connection is something called the estrobolome.
What Exactly Is the Estrobolome?
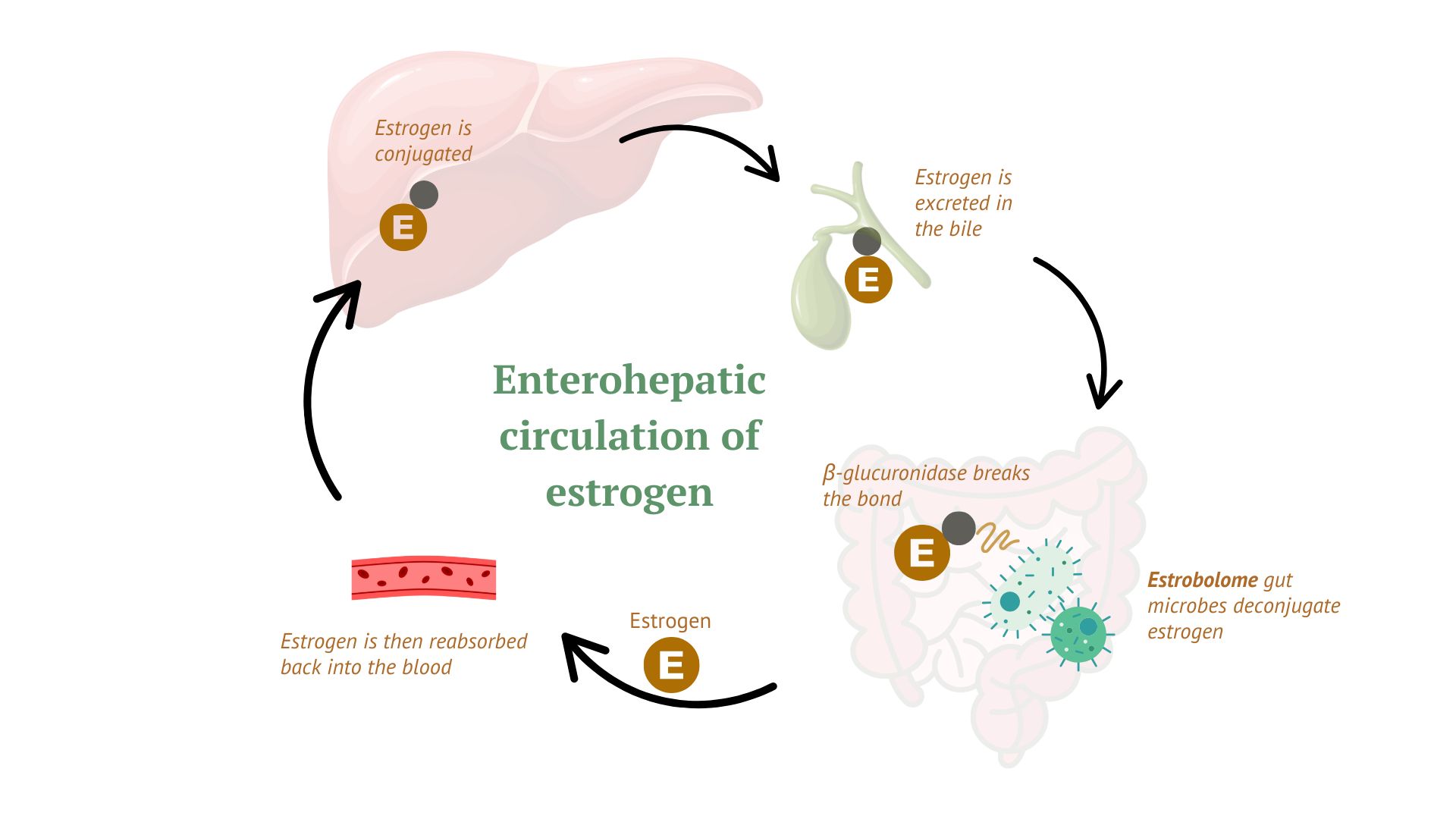
The estrobolome is the collection of gut microbes (and their genes) that can metabolize estrogens. These microbes produce enzymes, especially β-glucuronidase, which act like “unlocking tools” for estrogen.
Here’s how it works:
-
Your liver processes estrogen, making it water-soluble so it can be excreted in urine or bile.
-
Estrogen that enters the gut through bile is usually “locked up” (conjugated) and ready to be removed.
-
Microbes in the estrobolome can deconjugate, or “unlock,” this estrogen, reactivating it.
-
The reactivated estrogen is then reabsorbed into the bloodstream.
This recycling loop—called enterohepatic circulation—helps maintain balanced hormone levels.
Why Does This Matter for Women?
A healthy estrobolome provides just the right amount of recycling to keep estrogen in balance. But problems arise when there’s too much or too little β-glucuronidase activity:
-
Too much activity → More estrogen re-enters the bloodstream. This can raise circulating levels and increase the risk of estrogen-driven conditions such as breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and endometriosis.
-
Too little activity → Less estrogen is recycled. This may worsen low-estrogen states, as seen in menopause, contributing to symptoms like hot flushes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness.
Importantly, the relationship works both ways. Estrogen levels also shape which bacteria thrive in your gut, creating a feedback loop.
How the Gut Microbiome Changes After Menopause
Menopause is a time of profound hormonal change—and your gut feels it too.
Key Changes Seen in Studies
-
Reduced Diversity: Postmenopausal women have fewer different types of bacteria compared with premenopausal women.
-
Altered Composition: Helpful bacteria like Akkermansia, and Faecalibacterium decline, while other species become more dominant.
-
Reduced β-glucuronidase Activity: With fewer estrogen-reactivating microbes, less estrogen is recycled back into circulation.
-
“Male-like” Microbiome: The gut microbiome after menopause begins to resemble that of men—reflecting the shared low estrogen/progesterone environment.
What This Means for Health
-
Metabolic Risk: Lower microbial diversity and altered composition are linked to obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome.
-
Inflammation: Postmenopausal women often show higher levels of pro-inflammatory molecules (like IL-6), while producing fewer anti-inflammatory metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids.
-
Bone & Muscle Health: These gut changes may accelerate bone loss and muscle decline by affecting nutrient absorption and inflammation pathways.
The Diet–Gut–Estrogen Connection
Your daily food choices are one of the strongest levers for shaping your gut and its impact on estrogen.
-
Fibre: High-fibre diets nourish diverse bacteria and promote healthy estrogen metabolism. Whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and fruits all help.
-
Phytoestrogens: Found in soy, flaxseed, and legumes, these plant compounds can mimic estrogen in the body. Some gut microbes convert them into equol, a more bioactive form that may ease menopausal symptoms and protect against hormone-related cancers. Not everyone has the microbes to do this, but diet can help encourage them.
-
Fermented Foods: Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and other fermented foods provide beneficial bacteria that support gut balance and may influence estrogen levels.
-
Probiotics: Some observational studies link probiotic use with higher estrogen in premenopausal women and more favorable hormone ratios in postmenopause. Clinical trials are ongoing.
-
Antibiotics: While lifesaving when needed, antibiotics disrupt gut microbes, lowering β-glucuronidase activity and reducing estrogen recycling.
Supporting a Healthy Estrobolome and Gut After Menopause
The good news? You can take steps to support your gut and, in turn, your hormones.
-
Prioritise plant diversity → Aim for at least 30 different plant foods a week (fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, legumes, herbs, spices).
-
Include phytoestrogen-rich foods → Soy, flaxseed, chickpeas, and lentils can gently support hormone balance.
-
Enjoy fermented foods regularly → Even a spoonful of sauerkraut or a small glass of kefir daily can make a difference.
-
Exercise consistently → Movement supports both gut diversity and estrogen balance.
-
Sleep and stress matter too → Circadian rhythm and stress hormones influence your microbiome.
-
Use antibiotics only when necessary → Give your gut time to recover if you do need them.
The Bigger Picture
Your gut is not just a digestive organ—it’s a hormone regulator, immune trainer, and metabolic partner.
Through the estrobolome, your gut microbes play a vital role in estrogen metabolism, influencing whether hormones are recycled, reactivated, or excreted. After menopause, gut changes may contribute to inflammation, metabolic shifts, and bone health challenges—but they also highlight just how powerful lifestyle and diet can be in shaping your health.
By caring for your gut, you are not just improving digestion—you are directly influencing your hormone balance, reducing disease risk, and supporting a smoother transition through menopause and beyond.
Want my best free resources
Pop your name in and I will send you to my VIP resource page- more great gut tips included.
We hate SPAM. We will never sell your information, for any reason.
